Immigration Trends and Demographic Shifts: Implications for Society
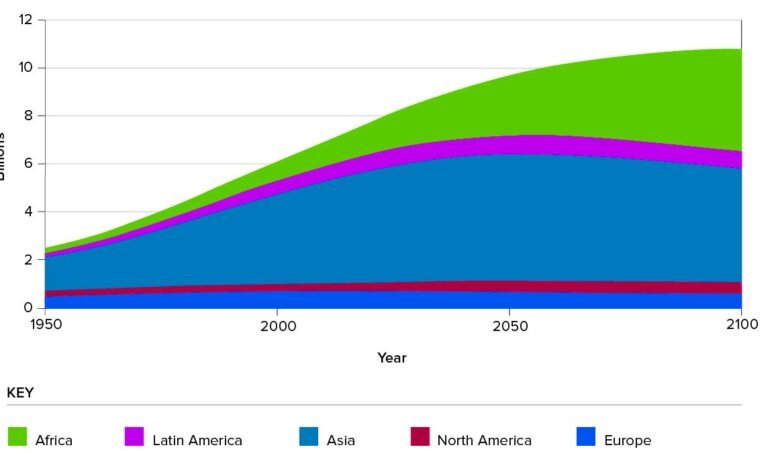
Immigration, a fundamental aspect of human history, continues to shape societies worldwide. The movement of people across borders influences demographics, economies, cultures, and politics. Understanding immigration trends and demographic shifts is crucial for comprehending contemporary society’s fabric and anticipating its future trajectory.
Historical Context of Immigration
Human migration traces back to ancient times, driven by factors such as trade, conquest, and seeking refuge from conflict or persecution. In the modern era, significant waves of migration occurred during periods of industrialization and colonization. For instance, the transatlantic slave trade and European colonization profoundly impacted demographic compositions, leading to cultural blending and social transformations.
Current Immigration Trends
In the 21st century, globalization has accelerated migration, facilitated by advancements in transportation and communication. Countries with robust economies often attract migrants seeking better opportunities, leading to diverse migration patterns. While some nations experience significant inbound migration, others witness emigration due to economic hardships, political instability, or environmental factors.
Demographic Shifts
Immigration is pivotal in shaping demographic profiles and altering age distributions, ethnic compositions, and religious affiliations within societies. In countries with aging populations, immigration contributes to demographic rejuvenation, replenishing the workforce and supporting social welfare systems. However, demographic shifts can also pose challenges, including social integration and cultural tensions.
Economic Implications
Immigrants are vital contributors to host country economies, filling essential roles in various sectors such as agriculture, construction, healthcare, and technology. Their labor often complements native workers, driving productivity and innovation. Moreover, immigrant entrepreneurs stimulate economic growth by establishing businesses and creating jobs. However, debates persist regarding the impact of immigration on wages, employment dynamics, and public services.
Cultural and Social Impact
Immigration enriches societies by bringing diverse perspectives, traditions, languages, and cuisines. Cultural exchanges foster creativity, tolerance, and mutual understanding. Yet, cultural clashes and social tensions can arise, stemming from differences in values, beliefs, and customs. Addressing cultural integration challenges requires efforts to promote inclusivity, mutual respect, and intercultural dialogue.
Political Ramifications
Immigration policies are inherently political, reflecting competing interests, ideologies, and public sentiments. Debates on immigration often intersect with broader discussions on national identity, sovereignty, and security. Political polarization and populism can fuel anti-immigrant rhetoric, leading to policy changes that affect immigrant communities’ rights and welfare.
Integration and Assimilation
Successful immigrant integration entails access to education, employment, healthcare, and social services. Language acquisition is a critical aspect of integration, enabling immigrants to communicate effectively and participate fully in society. However, barriers such as discrimination, xenophobia, and socioeconomic disparities can hinder integration efforts.
Global Perspective
Immigration is a global phenomenon, with countries adopting diverse approaches to managing migration flows. International cooperation and dialogue are essential for addressing migration-related challenges, including refugee crises, human trafficking, and labor migration. Multilateral agreements and frameworks seek to ensure human rights protection, fair labor practices, and sustainable development.
Read More: Immigration and Education: Promoting Inclusivity in Schools
Future Projections
Demographic trends indicate continued migration patterns driven by population growth, economic disparities, climate change, and geopolitical conflicts. Policymakers must anticipate future demographic shifts and develop strategies to address their implications for society. Proactive measures include promoting diversity, fostering social cohesion, and ensuring equitable access to opportunities for all residents.
Challenges and Opportunities
Immigration presents societies with both challenges and opportunities. Addressing social integration, economic disparities, and cultural tensions requires collaborative efforts from governments, civil society, and communities. Embracing diversity and inclusion can harness the benefits of demographic diversity, fostering innovation, resilience, and social harmony.
Policy Recommendations
Effective immigration policies should prioritize humanitarian principles, uphold human rights, and promote social justice. Comprehensive reforms should address legal pathways for migration, refugee protection, family reunification, and labor mobility. Moreover, policies must balance security concerns with respect for individual freedoms and dignity.
Community Engagement
Communities play a crucial role in fostering welcoming environments for immigrants. Local initiatives promoting cultural exchange, language learning, and community cohesion strengthen social bonds and reduce prejudice. Empowering immigrant communities through civic engagement and leadership opportunities enhances their integration and contributes to vibrant, inclusive societies.
Education and Awareness
Education is vital for promoting understanding and empathy towards immigrants. School curricula should incorporate multicultural perspectives, encourage tolerance, and combat stereotypes. Media campaigns, cultural events, and public forums facilitate dialogue and raise awareness about immigration issues, fostering solidarity and mutual respect.
Read More: The Ethics of Immigration: Justice, Rights, and Responsibilities
Conclusion
In conclusion, immigration trends and demographic shifts have profound implications for society. Embracing diversity, promoting inclusion, and addressing socioeconomic disparities are essential for building resilient and prosperous communities. By recognizing the contributions of immigrants and nurturing a culture of respect and acceptance, societies can harness the transformative power of immigration for collective well-being and sustainable development.
FAQs
How do immigration patterns vary across different regions?
Immigration patterns are influenced by factors such as geography, economic development, and historical ties. For example, North American and European countries often attract immigrants from Latin America, Africa, and Asia. At the same time, intra-regional migration is common in regions like Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
What are the economic benefits of immigration?
Immigrants contribute to economic growth by filling labor shortages, starting businesses, and paying taxes. Studies have shown that immigrants often complement the skills of native workers, leading to increased productivity and innovation.
How can societies promote immigrant integration?
Promoting immigrant integration requires investment in language training, education, and employment opportunities. Additionally, fostering intercultural dialogue and combating discrimination are essential for building cohesive and inclusive communities.
What role do immigrants play in addressing demographic challenges?
Immigrants often contribute to population growth and demographic rejuvenation in aging societies. By replenishing the workforce and supporting social welfare systems, immigrants can help mitigate the effects of declining birth rates and an aging population.
How can policymakers balance competing interests in immigration policy?
Policymakers must consider various factors, including economic needs, humanitarian concerns, and national security interests. Developing comprehensive immigration policies that prioritize fairness, compassion, and respect for human rights is essential for addressing the complex challenges of immigration.











